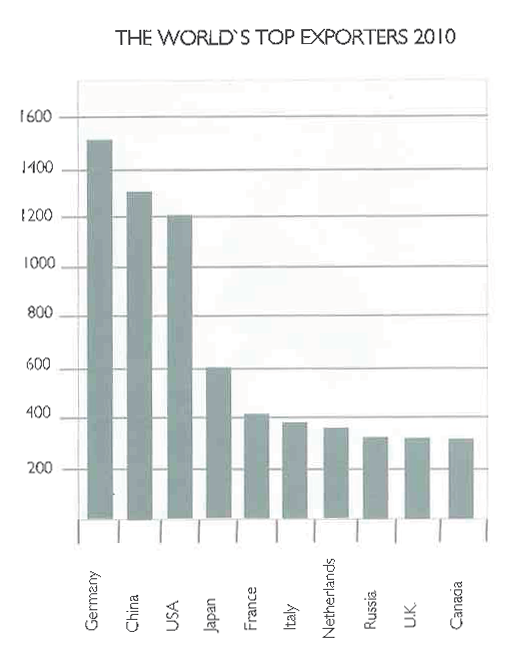
International trade is the exchange of goods and services between one country and another, but depending on how much each country exports or what are the goods that each country exports, the economy of that country can go better or worse.
Usually, MEDCs (More Economically Developed countries) export valuable manufactured goods such as electronics and cars and import cheaper primary products such as minerals, tea and coffee. In LEDCs (Less Economically Developed countries) the opposite is true. So, developing countries sell mainly raw, unprocessed and untransformed cheaper materials. While rich countries sell to them consumer goods such as technology and cars. And the trend in prices favours the rich countries: prices for raw materials are dropping, while manufactured products are still much higher.
Increasing trade and reducing their balance of trade deficit is essential for the development of LEDCs. However, sometimes MEDCs impose tariffs and quotas on imports. Tariffs are taxes imposed on imports, which makes foreign goods more expensive to the consumer. Quotas are limits on the amount of goods imported and usually work in the MEDC’s favour.
EXPORTS % 2010 BY REGIONS
Source: Wto: International trade statistics
- Europa: agricultural products, 9,2%; fuels and mining products, 10,7%; manufactured products, 80,2%.
- Africa: agricultural products, 8,3%; fuels and mining products 72,2%; manufactured products, 19,5%.
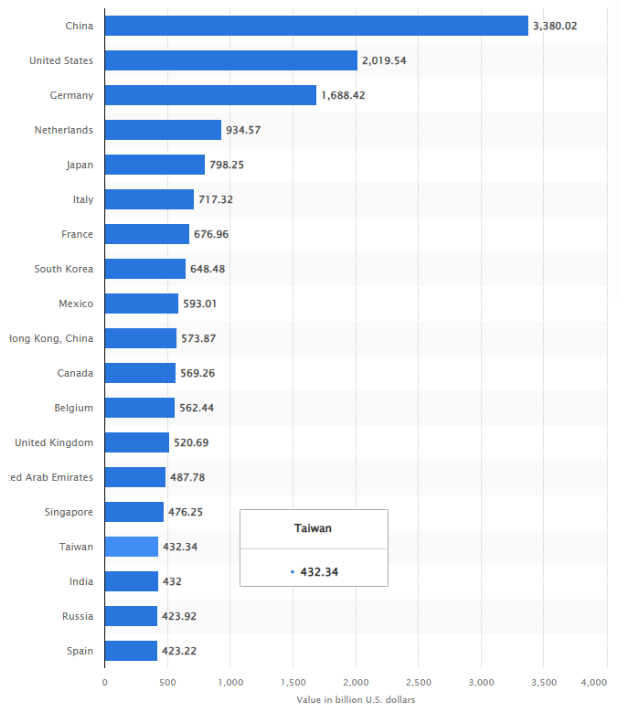
Leading export countries worldwide in 2023(in billion U.S. dollars)
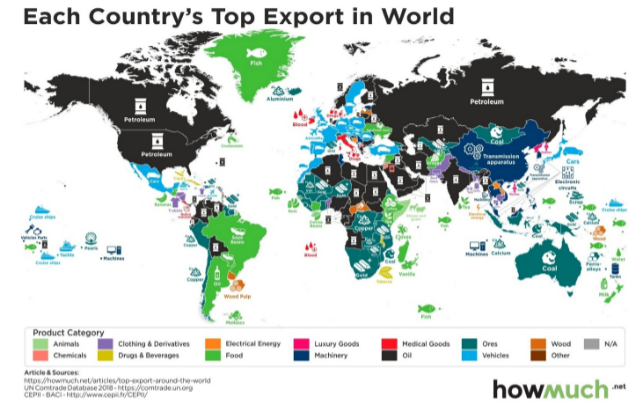
every-country-full-map.html