Regions sustained by commercial farming specialise in certain crops.
Most European farms are medium-sized family enterprises that require large capital investments. High standards of living mean that farms employ temporary labour.
In the part of Europe with an oceanic climate, meadow lands are exploited under intensive cattle raising. Cattle raising is found in all landscapes, especially when in the past the cattle was essential for fertilising fields. They are privately owned lands, and exploitation may be direct or indirect. In warmer regions, we may find vineyards and orchards.
In other regions there is no change and traditional farming is maintained: olives, wheat and vineyards.
In urban areas, vegetables and fruits for town markets are the main products and usually are multi-crop farmings.
In some areas such as United Stated or some regions of Russia, this commercial farming is done in large areas. These farms are family businesses that do not require a large workforce but are managed as companies.
Crops are produced for the market, not for home consumption.
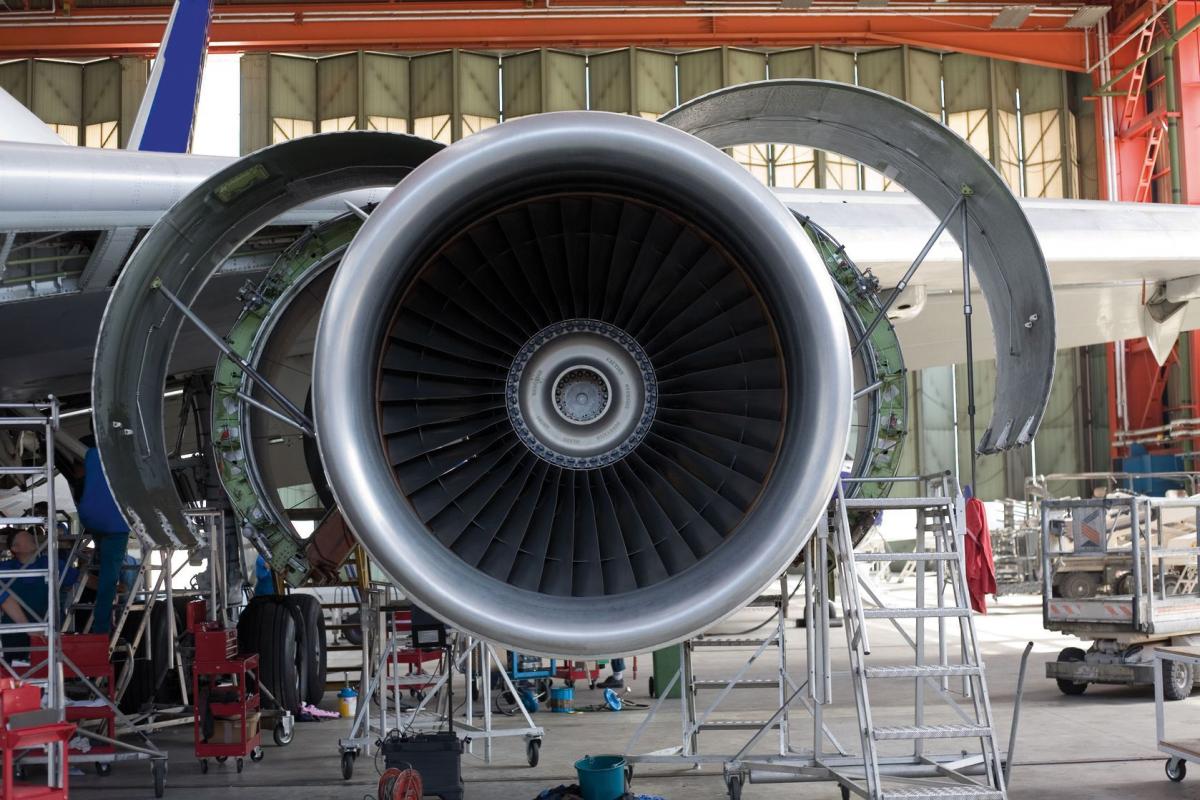
In North America farming is extensive with complete mechanisation. It covers wide areas and cultivates crops appropriate to each region: what, maize, cotton, tobacco. Land productivity is not high but production is cheap, because they use little labour and a lot of machinery.
Property is privately owned and cultivation is direct. Agriculture uses all the mechanical, technical and scientific advances required by the green revolution. They achieve great profitability although they make the biggest money investments in the world to attain it.
Single-crop cultivation predominates.
The Russians regions show a similar landscape. They are large exploitations with a lot of mechanisation. Single-crop farming is specialised region by region.