The mining and the forest exploitation are the least important activities of the primary sector. These activities are carried out close to mineral mines and forests. On the one hand, the mining get raw materials for buildings or road (for instance stones) and on the one hand minerals like magnesite for fertilizers. The most of the forest exploitation establishments are located in Navarre, because there are in this province the most of the forests (Irati, Urbasa, …)
Category: Social Sciences
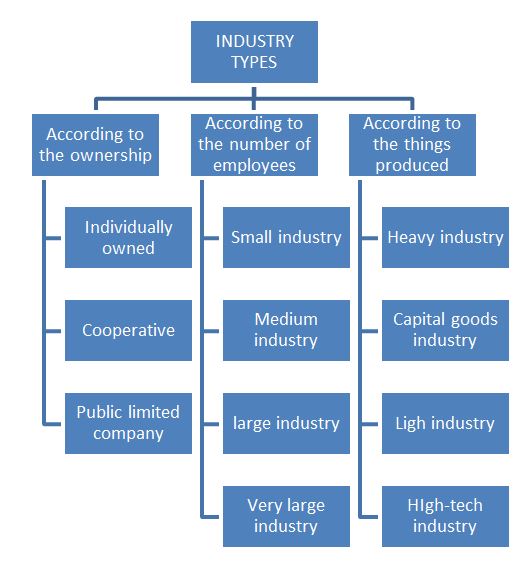
Light industry
Also called consumer goods industry, provides finished products for direct consumption by the population.
Characteristics
- It transforms goods for direct consumption by transforming products of basic industries or agriculture / fishing…
- Food, textile, automobile (cars and car parts) , light chemical products (cosmetic, plastic..) are examples of this.
- The food industry is the most important of these. The freezing or tinning of transformed agricultural products has become highly developed, bringing with it changes in eating habits.
- Electronic industries are mobile phones, computers, calculators, stereos and televisions
- Usually located near large cities and transport links.
- Needs fewer raw materials and energy resources than heavy and capital goods industry.
- They also tend to be less polluting.
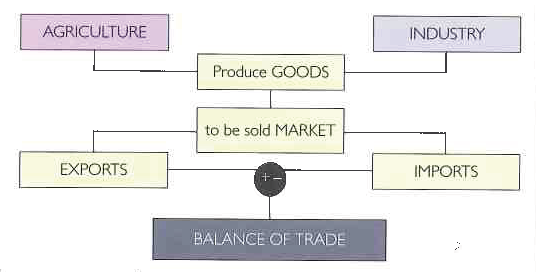
International trade: exports
International trade is the exchange of goods and services between one country and another, but depending on how much each country exports or what are the goods that each country exports, the economy of that country can go better or worse.
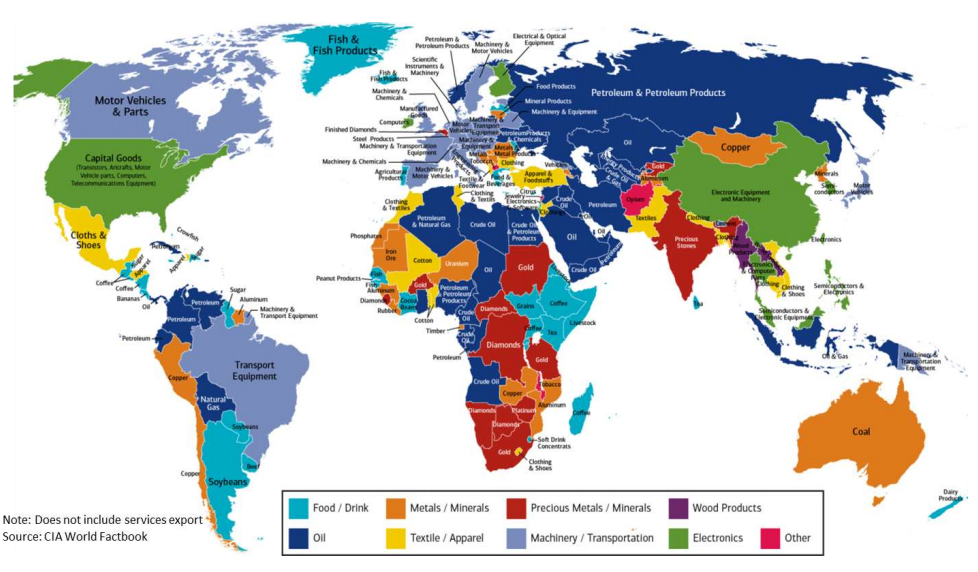
Usually, MEDCs (More Economically Developed countries) export valuable manufactured goods such as electronics and cars and import cheaper primary products such as minerals, tea and coffee. In LEDCs (Less Economically Developed countries) the opposite is true. So, developing countries sell mainly raw, unprocessed and untransformed cheaper materials. While rich countries sell to them consumer goods such as technology and cars. And the trend in prices favours the rich countries: prices for raw materials are dropping, while manufactured products are still much higher.
Increasing trade and reducing their balance of trade deficit is essential for the development of LEDCs. However, sometimes MEDCs impose tariffs and quotas on imports. Tariffs are taxes imposed on imports, which makes foreign goods more expensive to the consumer. Quotas are limits on the amount of goods imported and usually work in the MEDC’s favour.
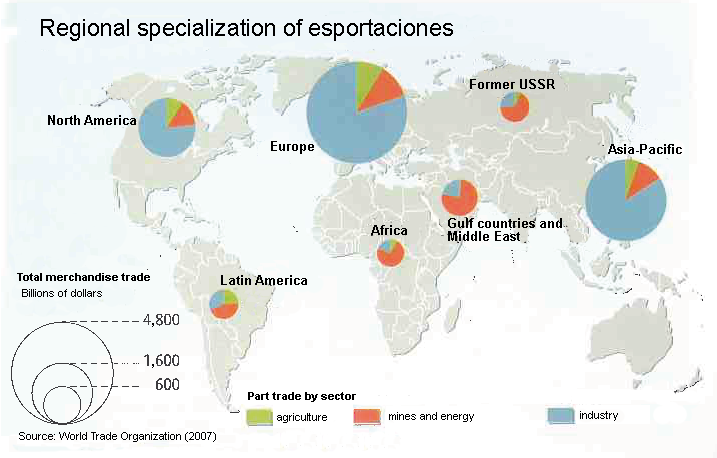
EXPORTS % 2010 BY REGIONS
Source: Wto: International trade statistics
- Europa: agricultural products, 9,2%; fuels and mining products, 10,7%; manufactured products, 80,2%.
- Africa: agricultural products, 8,3%; fuels and mining products 72,2%; manufactured products, 19,5%.
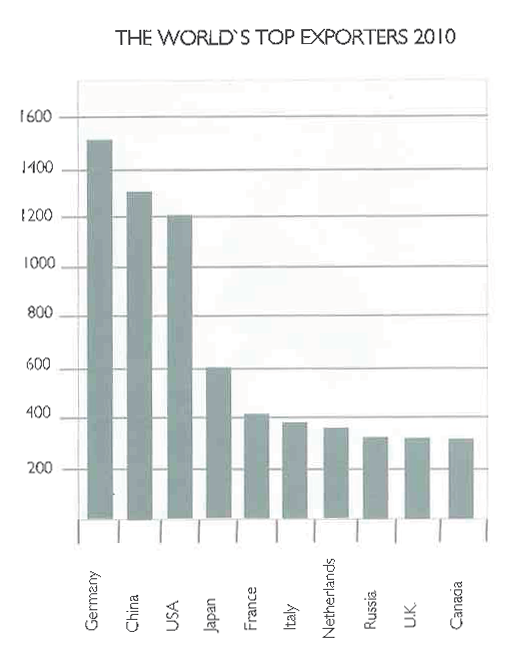
Leading export countries worldwide in 2023(in billion U.S. dollars)
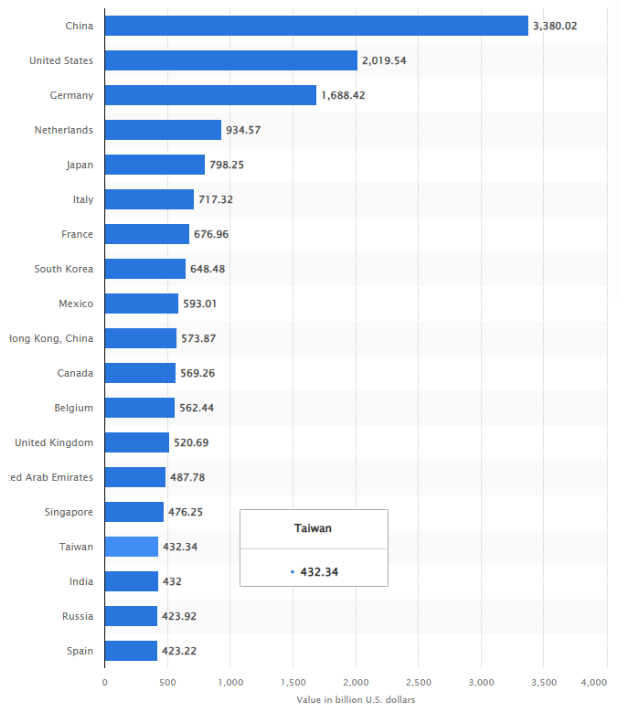
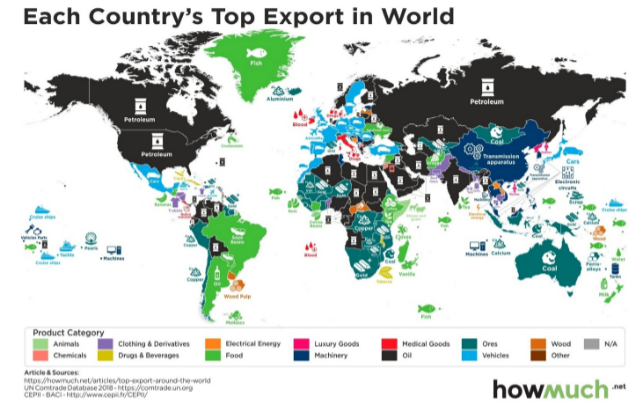
every-country-full-map.html
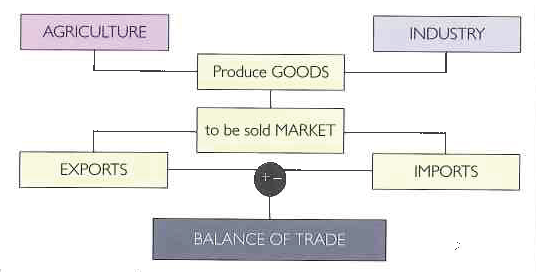
International trade: balance of trade
Trade balance is the difference between the values of the products that a country sells to other countries (exports), and the cost of the goods that the country buys from abroad (imports) during a particular period (commonly a year).
A trade surplus means that the value of exports is greater than imports. A trade deficit is when there are more imports than exports.
Another useful data is the balance of payments of a country that consists of the record of all economic transactions between the residents of a country and the rest of the world. To calculate it we add to the trade balance, the services, the capital movements (money spend by tourists, sent home by emigrant workers.. and the financial transactions (investments, buys of foreign companies…).
If a country has higher incomes than payments, the balance of payments will be positive and if a country has higher payments, the balance of payments will be negative.
If a country has a negative balance trade, it owes money to other countries, because that means that needs to pay more than it collects and it’s say that country has an external debt.
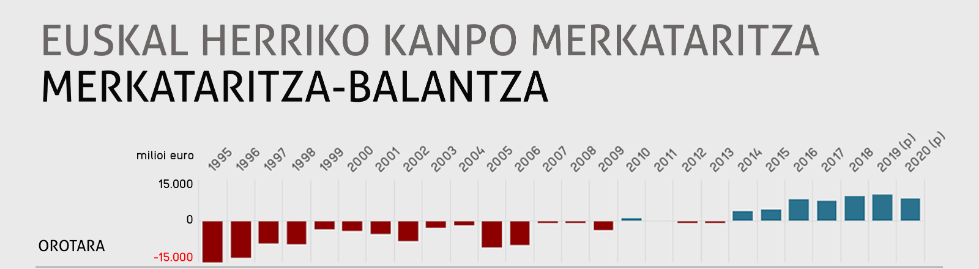
Foreign trade of the Basque Country. Balance of Trade
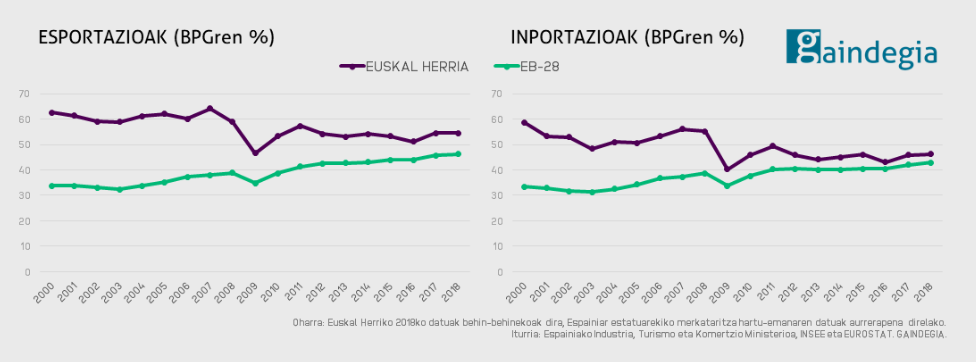
Development of Exports and Inports Basque Country and Europe
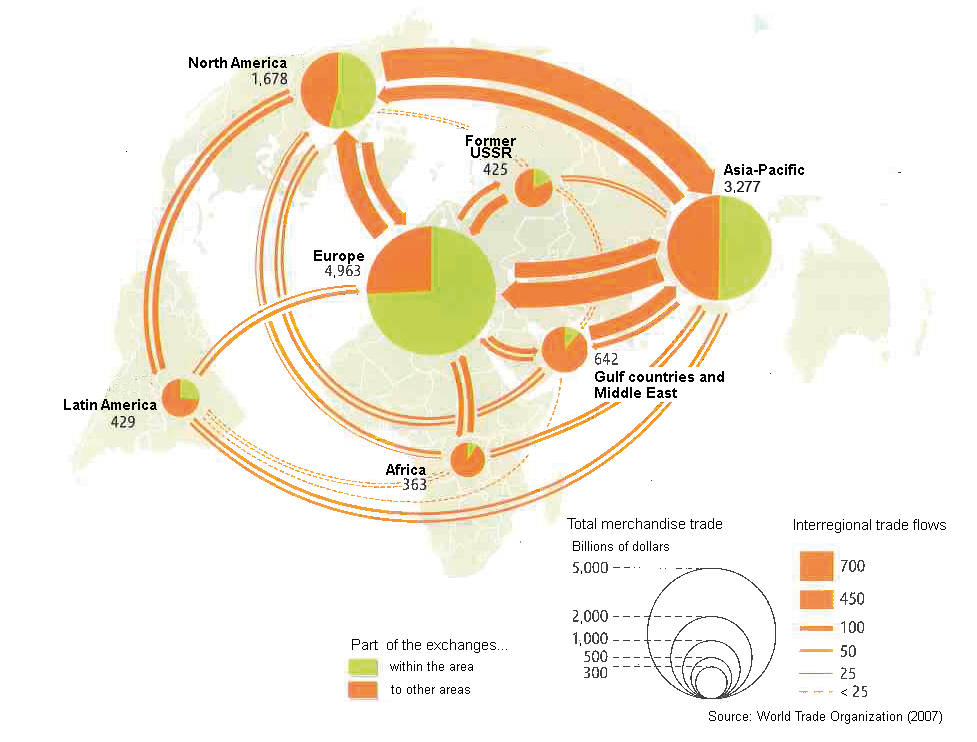
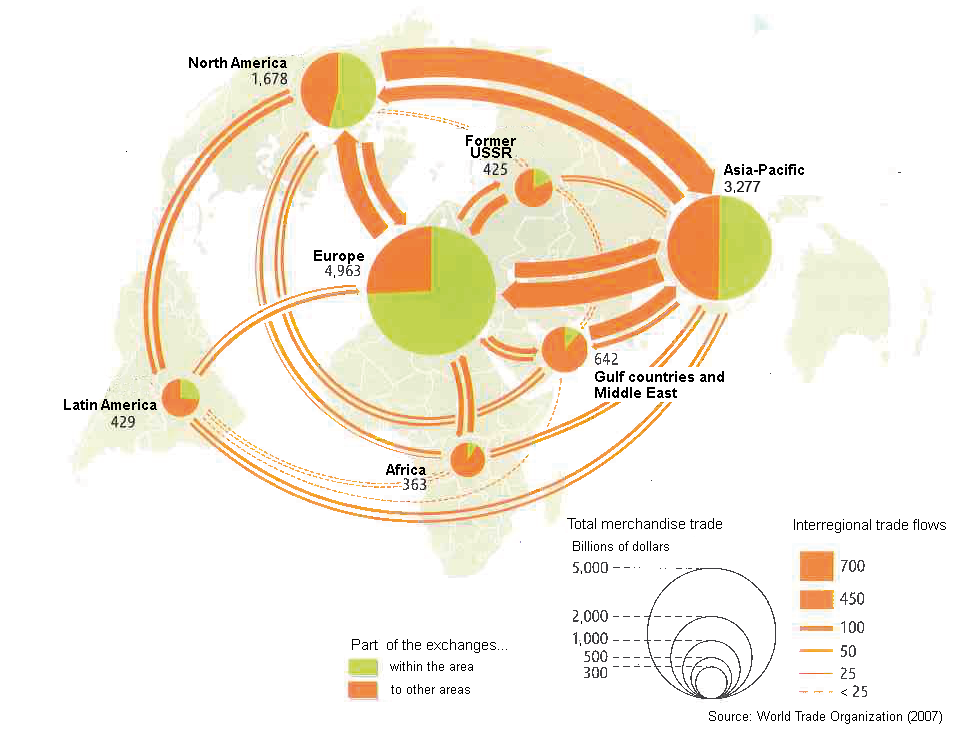
International trade: The world market
International trade is the exchange of goods and services between one country and another.
International trade has been present throughout much of history, starting from the Mediaeval Silk Road or the Transoceanic Trade between Europe and America during the Modern Era, after Europeans arrived to America.
Anyway, the economic, social, and political importance of the international trade has been on the rise in recent centuries.
Nowadays, Mutual dependence between national economies is increasing constantly as international trade grows. Between 1980 and 2010, world trade multiplied by a factor of four. The developed, industrialised countries (Western Europe, USA, China, Canada, Japan…) control 80% of the world trade.
Today, since we all produce, distribute and use products from all over the world, the international economy is like one great market. In this growth of economic relations between countries, the multinationals are particularly influential.
The most highly developed countries, together with suppliers of certain raw materials such as petroleum and coffee, are the ones with the most trade.
This imbalance contributes t the economic dependence of some countries (mostly developing countries) upon other, developed, countries.
In the resulting situation of inequality between different parts of the world, the developed countries have a double advantage. Not only do a number of transnational / multinational companies have the highest sales figures in the world, bur furthermore their economic strength gives those companies extraordinary power.
Walmart, for example, is the world’s powerful company and the biggest private employer in the world with 2,2, million employees working on 11.500 stores in 27 countries. This retail stores sell food, clothes and almost everything. Its annual revenues (US$ 20.428 billion in 2024), for example, exceed the GDP (the gross national product) of any developing country… Austria United Arab Emirates, Denmark, and Qatar…
International trade
International trade is the exchange of goods and services between one country and another. In most countries such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product (GDP).
International trade has been present throughout much of history, starting from the Mediaeval Silk Road or the Transoceanic Trade between Europe and America during the Modern Era, after Europeans arrived to America.
Industry types
High-technology industry
High-technology (or high-tech) industry refers to industries whose processing techniques usually involve micro-electronics.
Characteristics:
- These modern factories often have their own research and development units.
- They are freer to choose their location but they like to be located near to motorways and airports.
- They need very few people, but highly qualified and skilled workers.
Heavy industry
Also called basic industry. It transforms raw materials into semi-finished products that are then used in other industries, and includes mining and energy production.
Characteristics:
- Coal, iron, copper, bauxite, petroleum or natural gas is some of the chief raw materials used in this industry.
- Metallurgical or siderurgical industry and heavy chemical industry are examples of this.
- Iron and steel making, the prototype of heavy industry, is the transformation of iron ore into pig iron or steel.
- Chemical industries transform mining products into other goods, for use in other industries.
- Usually located near mines, and energy sources, or near ports of entry for raw materials to reduce the transportation price of raw materials.
- Very polluting, usually are located outside cities or in countries with permissive environmental laws.
- Requires high investment in raw materials and energy sources.
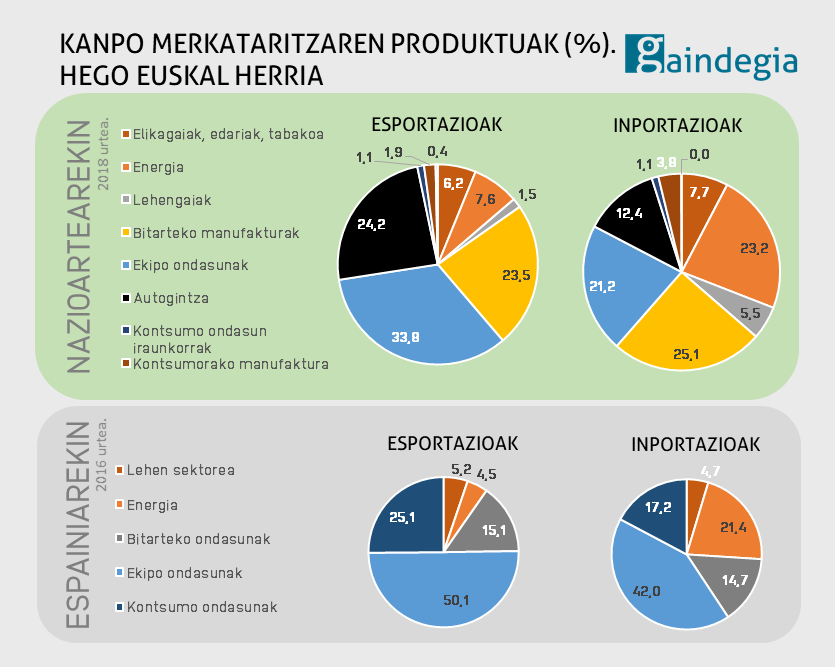
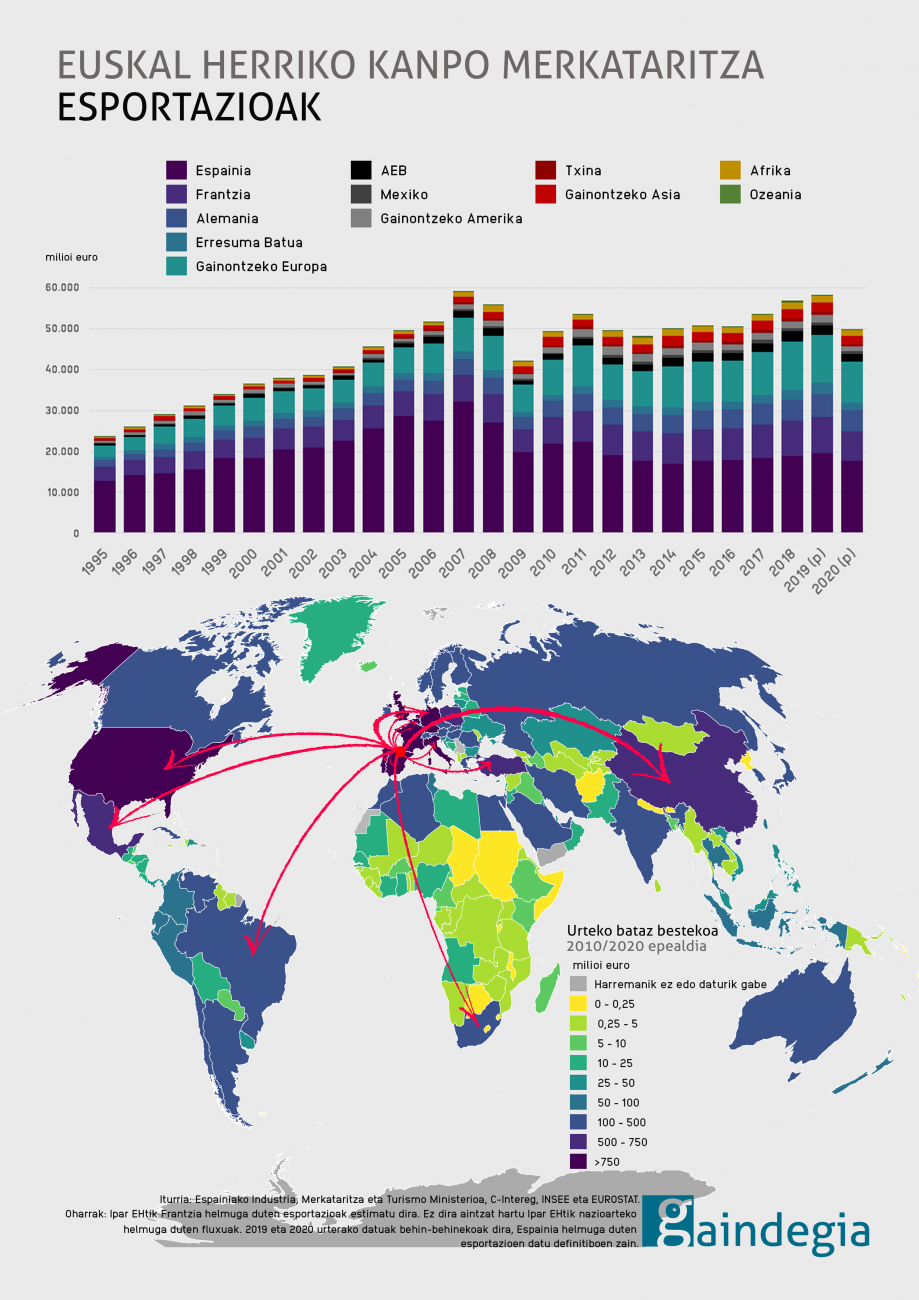
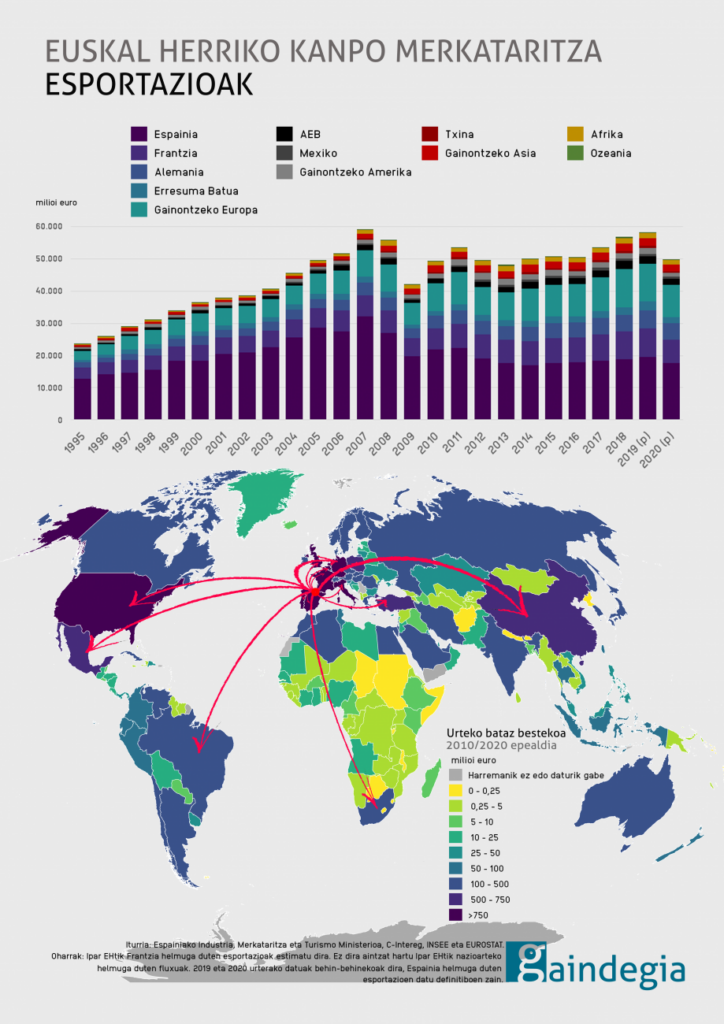
International Trade: Commercial Relations Between the World and the Basque Country
Basque Country’s Trade in 2020
In 2020, the Basque Country maintained trade relations with the majority of countries worldwide (three-quarters of them). In most cases, exports were worth more than imports. However, the negative trade balance with China (where the Basque Country buys more than it sells) continued to grow.
Impact of COVID-19
The pandemic severely affected the global economy. Exports dropped significantly, with a 14.5% decline in the Basque Country. However, China and a few other countries managed to increase their exports during this period.
Basque Exports
Exports accounted for 50% of the Basque Country’s GDP in 2020. About 73% of Basque exports were
directed to Eurozone countries, mainly France, Germany, the United Kingdom, and Belgium.
In the Southern Basque Country, the most exported products included:
- Capital goods, particularly industrial machinery, electrical devices, and transportation vehicles (37%)
- Car parts (23%)
- Manufacturing materials, mainly iron and steel, wheels, paper, and plastic (23%)
There is limited data on exports from the Northern Basque Country, but the most exported products are food and goods related to the aeronautics sector.
A significant portion of Basque exports goes to Spain, but this dependency has decreased in recent decades. Basque companies have made efforts to expand internationally over the past ten years, gaining new customers in the USA, Mexico, China, Turkey, Brazil, and South Africa.
Trade Balance
In general, the Basque Country exports more in value than it imports, leading to a positive trade balance. However, the negative trade balance with Spain, China, and Ireland is particularly high, amounting to €1.06 billion and €495 million, respectively.
The Basque Country imports heavily from China, purchasing industrial machinery, electronic devices, telecommunications equipment, chemicals, and plastics. This creates competitive challenges for Basque businesses.
Additionally, due to energy-related imports, the Basque Country has a negative trade balance with several countries, including Russia, Kazakhstan, Taiwan, and Libya.
A New Economic Landscape
The future of the economy remains uncertain, and Europe must find its place in the global market. Meanwhile, Asia is becoming increasingly influential in the world economy. The Basque Country will need to adapt to these changes in the coming years.
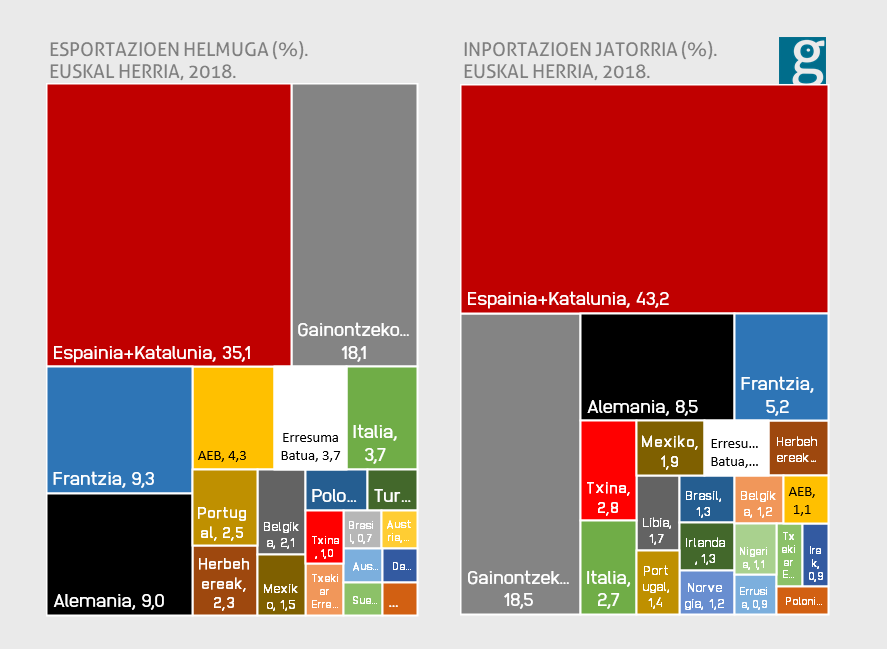
Foreign trade of the Basque Country. Export
herriko-esportazioak-munduan.png?itok=sxsSFDy2